Avalanche Granite Upgrade - Enhancing Interchain Messaging, Unlocking Biometric Use Cases, and Enabling Dynamic Block Times
Granite is a major Avalanche upgrade that improves cross-chain messaging, adds biometric-grade crypto, and boosts L1 performance.
The Avalanche ecosystem has entered a new phase of performance and scalability with the release of the Granite upgrade, one of the network’s most significant enhancements.
Granite introduces breakthrough improvements across consensus performance, network resource efficiency, and developer usability, further strengthening Avalanche’s position as the fastest and most customizable blockchain ecosystem.
In this article, we break down what Granite brings to builders, validators, and users, and why this matters for the future of the Avalanche network.
What Is Granite?
Granite is the latest avalanche upgrade driven by three Avalanche Community Proposals that introduce enhancements at the following levels:
Robustness and cost-effectiveness of Interchain Messaging (ICM): ACP-181: P-Chain Epoched Views
Security and user experience: ACP-204: Precompile for secp256r1 Curve Support
Transaction Finality: ACP-226: Dynamic Minimum Block Times
These changes optimize how nodes synchronize, validate, and process transactions across L1s.
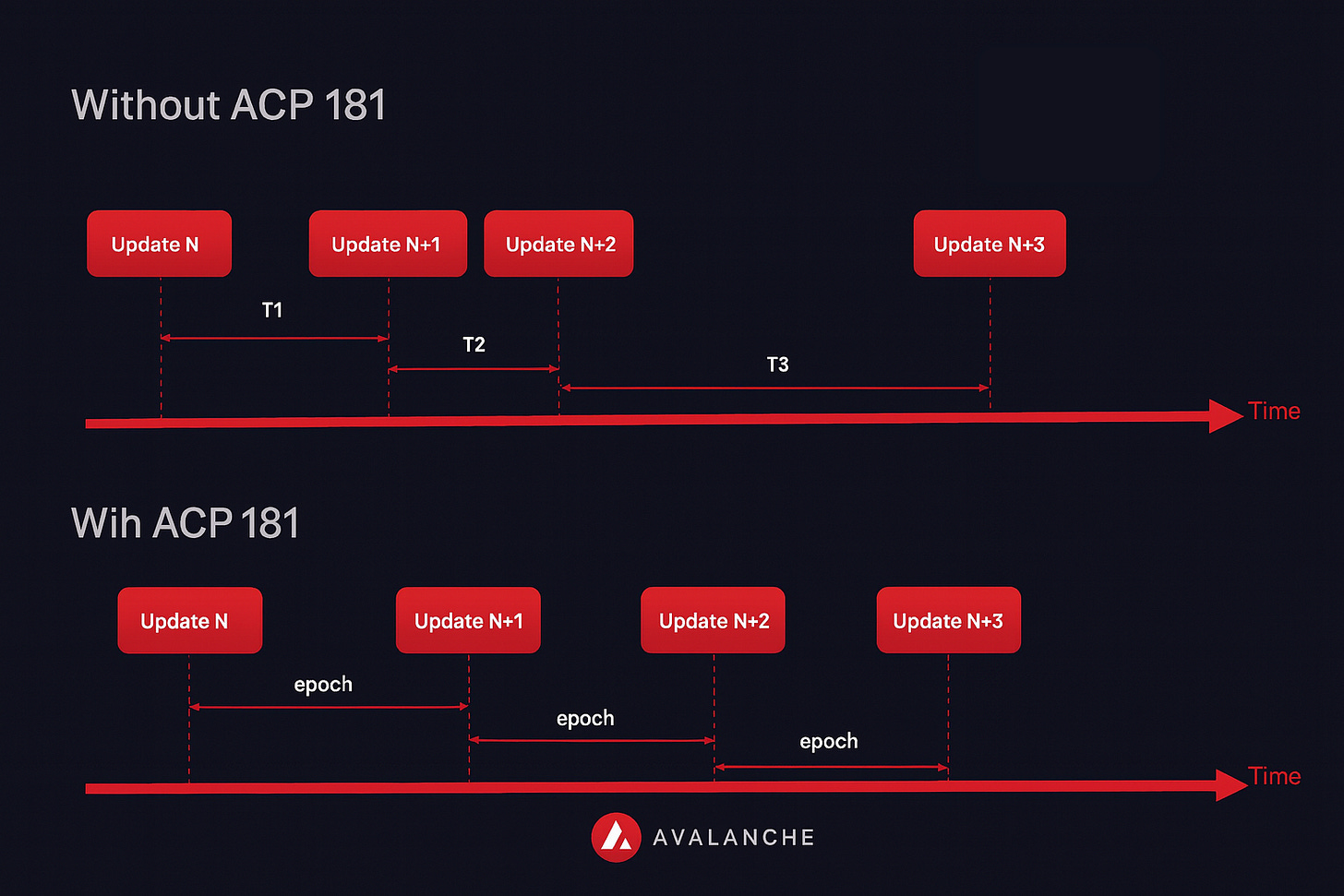
ACP-181: Epoched P-Chain Views for More Efficient ICM
Interchain Messaging (ICM) is one of Avalanche’s most powerful interoperability components, enabling L1s to exchange verified messages trustlessly via the P-Chain. But verifying these messages efficiently and reliably has always been a challenge due to the change of the P chain height and the validator set every block, causing:
ICM messages could be invalidated between block changes
Cross-chain verification logic had to recompute trust proofs
Costs increased due to inconsistent validation references
Granite’s Solution: Epoched Validator Views
When an L1 wants to trust messages from Avalanche’s P-Chain, it needs a stable picture of who the validators are. If validator info can change every block, the “picture of the network” is constantly moving, which makes verification more complex.
Instead of letting the validator set change on every block, Avalanche groups time into short periods called epochs (around 5–10 minutes).
For each epoch, the P-Chain takes a “snapshot” of the validator set and keeps it fixed for the whole epoch.
All cross-chain messages (ICM) sent during that epoch refer to this same snapshot.
That means L1s only need to trust and verify one stable view of the network for that whole period, which makes cross-chain verification simpler, faster, and easier to reason about.
Why this matters
Fewer invalidated messages → More reliability for cross-chain apps.
Predictable validator view → Easier to build on.
Lower verification cost → Less computation and overhead.
Better UX → Fewer failures and retries for cross-chain requests.
ACP-204: Enabling Biometric Authentication with secp256r1 Curve Support
As blockchain adoption expands beyond crypto-native users, authentication methods must evolve. secp256r1 is the cryptographic backbone of modern biometric authentication, enabling fingerprint, face recognition, and secure hardware key signing.
Granite Makes Avalanche Biometric-Ready
With ACP-204, Avalanche introduces native precompile support for secp256r1 signatures. This means smart contracts on Avalanche can verify signatures created by mobile devices and hardware-based identity systems, without relying on off-chain verification.
The impact:
This improvement to the signature process unlocks:
Passwordless onboarding: Users can authenticate to an Avalanche application using Face ID, Touch ID, or Passkeys.
Safer user experience: Biometric-backed cryptographic signatures provide more secure hardware-level key isolation and reduced risk of key compromise
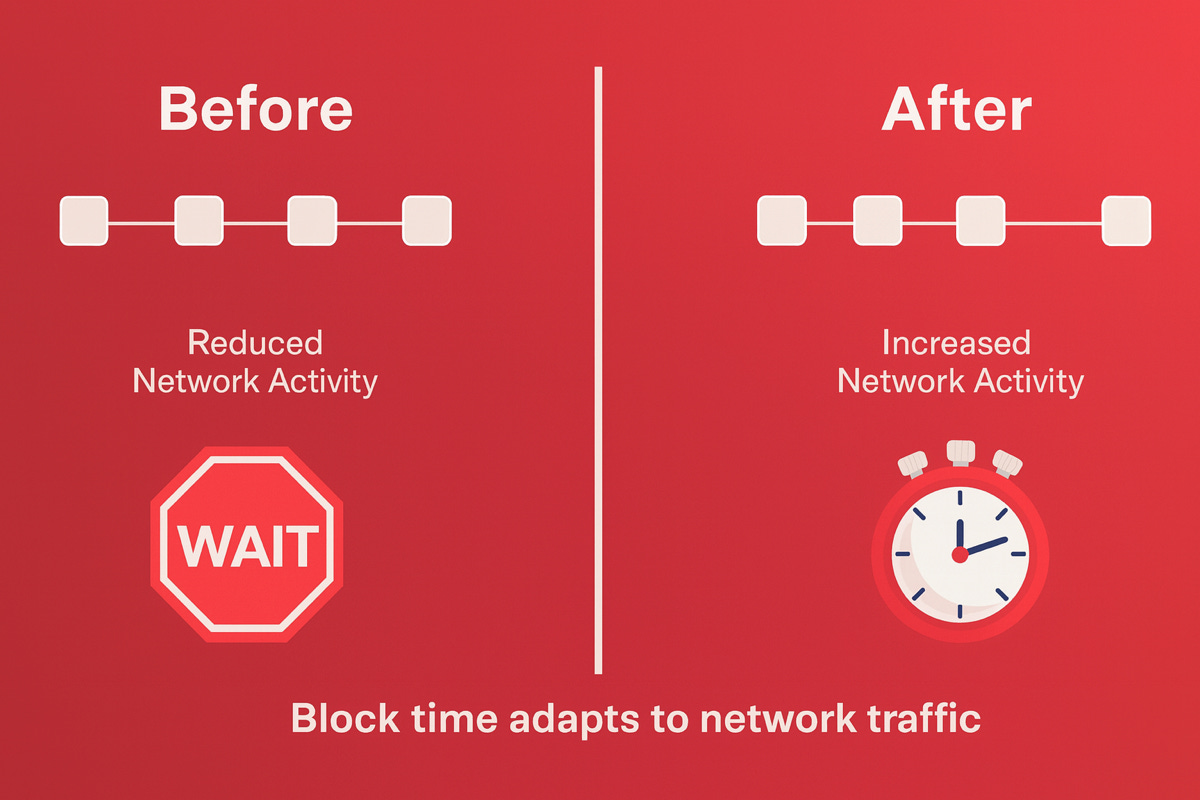
ACP-226: Dynamic Minimum Block Times for Faster, Adaptive Networks
Avalanche is already known for sub-second finality, but its configurability is what sets it apart. With ACP-226, L1s gain even more flexibility over block production.
Previously, L1s operated with a fixed minimum block time. While stable, it created two limitations:
Throughput could be underutilized during high activity
Latency couldn’t be optimized dynamically
Low-activity periods produced unnecessary empty blocks
Granite Introduces Dynamic Minimum Block Times
With the Activation of ACP226, validators will dynamically adjust block times in response to network conditions (Network congestion, Validator performance...). This flexibility enables:
Faster transaction confirmation: block times shrink under load, enabling faster confirmation during busy periods.
Optimise resources: During quiet hours, validators can adjust block times without network upgrades, reducing compute and storage use
Future-proof scalability: enabling dynamic block times lays the foundation for continuous performance improvements, allowing the network to adapt and scale as transaction volumes grow
Bringing It All Together: Why Granite Matters
The Avalanche Granite upgrade marks a major step forward in building the next generation of scalable, secure, and developer-friendly blockchain infrastructure.
For developers, Granite unlocks cheaper and more predictable cross-chain messaging, introduces modern authentication capabilities through secp256r1, and provides faster, more flexible performance tuning across L1s.
For node operators, it delivers greater stability, clearer epoch boundaries, and upgraded cryptographic foundations, ensuring the network remains secure and future-proof as it scales.
Granite lays the groundwork for what comes next, empowering Avalanche to support richer applications, higher throughput, and a more seamless cross-chain ecosystem.
Getting Involved
If you’re ready to go deeper into ACPs, here are a few ways you can get involved:
Join ACP meetings: Sign-up form
If you have an idea to improve the network, propose an ACP yourself: ACP Proposal Template
ACPs repository: GitHub repository
Dive into the Avalanche ecosystem today! Download the Core Wallet and unlock a world of seamless DeFi, NFTs, and more.








Always cooking 🔺🔥